Idempotency
The idempotency strategy is widely applied to avoid, for example, the collection of a duplicate payment received in the API. To better visualize, we are talking about the request with a POST/PUT/PATCH command or an event that arrives duplicated by the Stream.
Some Stream services sometimes send duplicate messages to ensure high delivery speed, and this forces applications to control idempotency.
Devprime offers a very flexible approach to service configuration that can be configured to start automatically, per parameter sent by the consumer, and/or restricted to specific processes according to each microservice’s strategy.
The idempotency feature can be configured to work automatically using the “action” parameter as “auto” and the “flow” parameter as “backend” enabling the feature without the need to pass a foreign key when consuming the API.
To better visualize the scenario in practice, it is essential to follow the sequence of images where we demonstrate the entire process in the Log. Auto-Logging is generated by the native Servability approach.
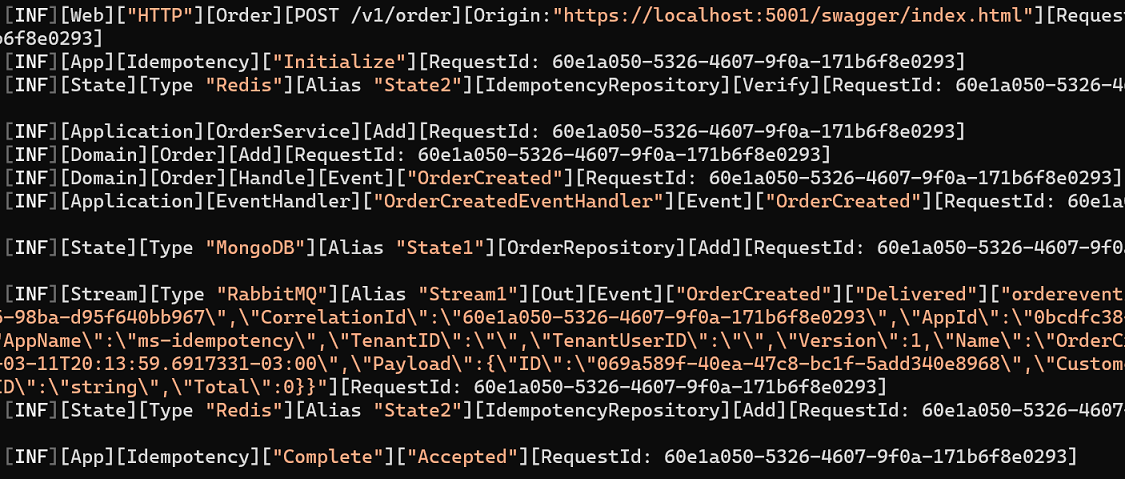
Making the First Post to the Orders API
When you examine the log, view the idempotency information as active in that request, initiating duplicate protection.
Make a second post in the Requests API identical to the previous one
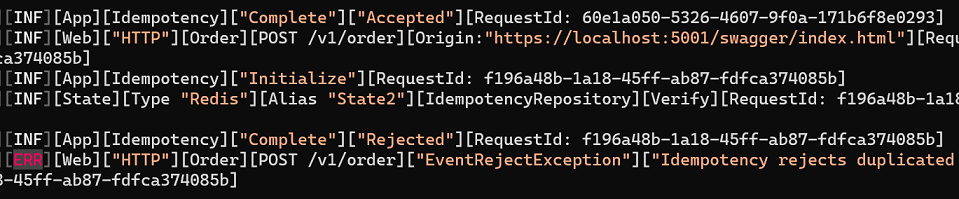
Right now we are repeating the scenario, only now we will have another answer in the control of idempotency.
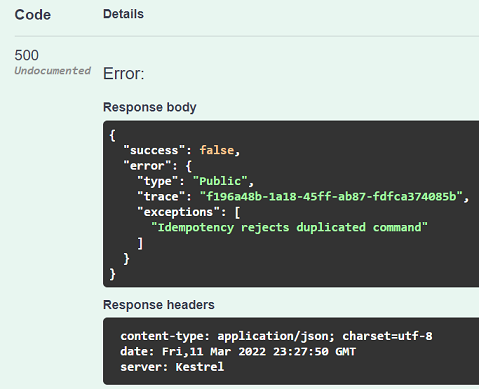
When analyzing the API result, we see the duplicate request decline
When you look at the Log in the idempotency section you will find the “Reject”
Two-step configuration of idempotency
Setup is a simple and customizable process
Enable Idempotency on the “Devprime_App” key by setting the “Enable” value to “true”.
|
|
Add a second Redis persistence in the “State” key for idempotency automatic transaction control information.
|
|
Activating idempower manually
In the desired scenarios, you can manually configure idempotency support.
|
|
You’ve just checked out a powerful feature present in Devprime Stack. Use the Devprime platform to accelerate the journey of application modernization and digital platform development.
More details on deidempotency scenarios
Implementing idempotency in microservices
Idepotency in microservices and REST APIs
Implementing idempotency in microservices